Glass Thermometers in IoT: Old-School Accuracy Meets Smart Connectivity
When you think of thermometers, chances are the old-school glass type comes to mind. These slim tubes filled with mercury or colored alcohol were once the standard way of checking temperature—whether in classrooms, labs, or even in our homes. While digital sensors dominate most IoT applications today, it’s fascinating to see how even glass thermometers still have lessons to offer in the connected world.
A Quick Refresher: How Glass Thermometers Work
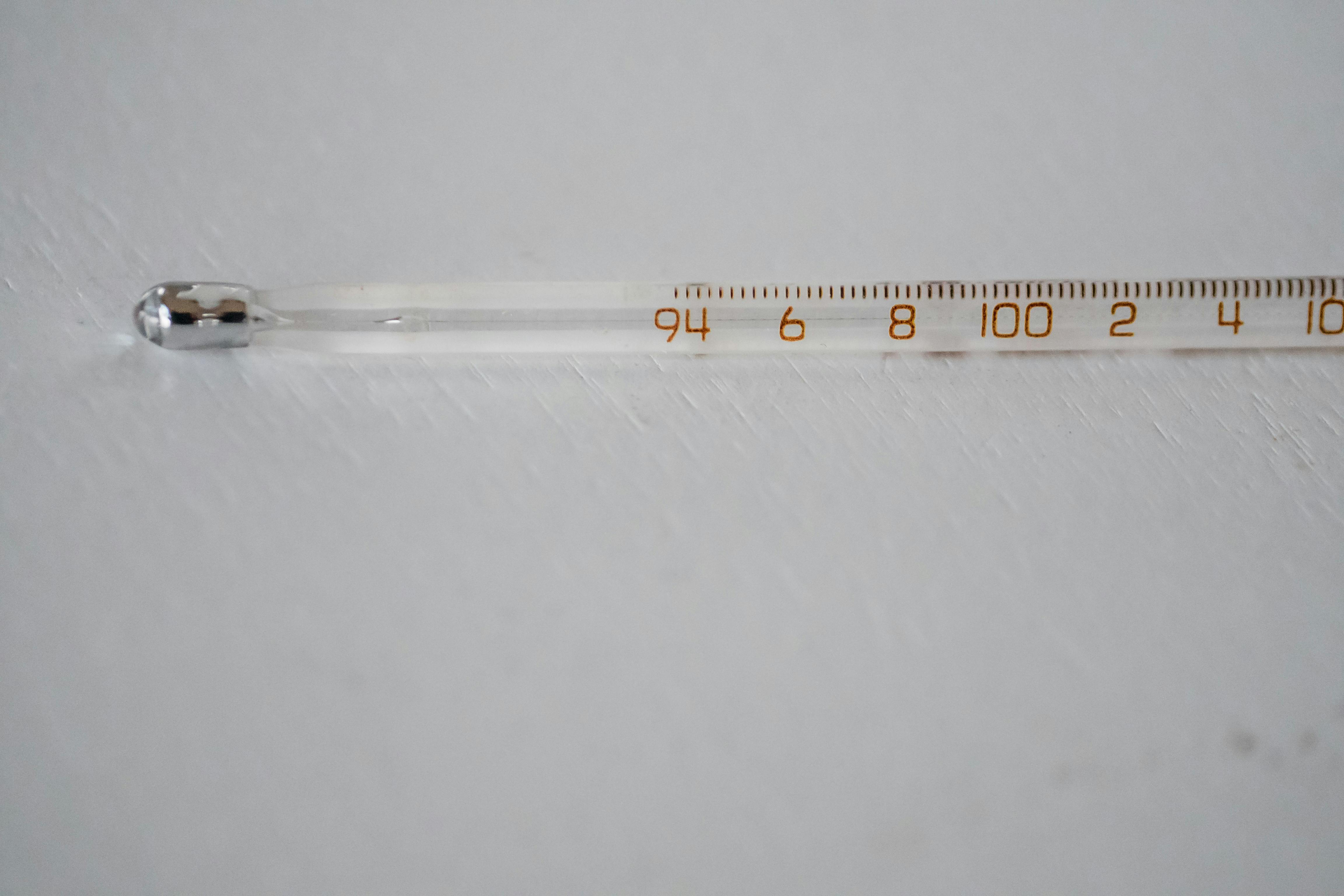
Glass thermometers rely on the simple principle of liquid expansion. As temperature increases, the liquid (often mercury or alcohol) expands and rises in the narrow glass tube. When it cools, the liquid contracts and moves back down. The scale on the tube tells you the temperature reading.
It’s a design that has stood the test of time because of its accuracy and simplicity. No batteries. No wiring. Just physics in action.
But Where Do They Fit Into IoT?
At first glance, glass thermometers might seem outdated in an IoT-driven world filled with digital sensors, wireless modules, and smart dashboards. However, they can still play a role when combined with modern technology. Here’s how:
- Calibration Tools: Used to double-check or calibrate digital IoT sensors for accuracy, especially in sensitive industries like food processing or pharmaceuticals.
- Hybrid Systems: Some IoT setups use optical or camera-based readers to track the liquid level in glass thermometers and transmit readings digitally.
- Low-Tech Environments: In rural or resource-limited areas, glass thermometers can act as a backup where electronic sensors may fail.
Real-World Examples
- Cold Chain Monitoring: Vaccine transport systems sometimes pair glass thermometers with IoT trackers, combining digital alerts with physical checks.
- Greenhouse Management: Farmers in resource-limited regions pair glass thermometers with simple IoT cameras to digitize readings for remote monitoring.
- Educational Labs: IoT-enabled science kits include glass thermometers to compare classic methods with modern sensors.
The Challenges
Of course, glass thermometers are not perfect for IoT:
- Mercury-based ones raise safety concerns due to toxicity.
- They are fragile and can break easily.
- They don’t provide instant digital output, which IoT systems thrive on.
Looking Ahead
Glass thermometers may no longer be the star of the show, but they remind us of the roots of temperature measurement. In IoT, they serve as reliable backups, calibration references, and educational tools. Pairing their simplicity with IoT’s intelligence creates systems that are both trustworthy and future-ready.
In a way, glass thermometers represent the perfect balance: the old world of analog precision meeting the new world of smart connectivity.